Plastic tanks for the storage and subsequent use of rainwater. Due to various roof shapes and coverings, not all rainwater is drained off the roof. This is expressed by the “drainage coefficient” (0.6 to 0.8). When rainwater comes in contact with the roof, it may get contaminated, and therefore not all roofs are equally suitable for the collection of rainwater.
Roof - collects rainwater
Due to various roof shapes and coverings, not all rainwater is drained off the roof. This is expressed by the “drainage coefficient” (0.6 to 0.8). When rainwater comes in contact with the roof, it may get contaminated, and therefore not all roofs are equally suitable for collection of rainwater.
Why use rainwater?
-
The price of potable water keeps rising
-
Sources of good-quality potable water are limited and not available everywhere
-
Rainwater is “soft” water, which means that it is convenient for:
-
washing, as its use reduces the consumption of washing powder
-
WC and pipelines, as it does not cause an accumulation of scale
-
the irrigation of indoor plants and the garden, since it does not contain chlorine or other substances
How to use rainwater?
Rain
- falling on built-up areas is usually drained into the sewerage system without being used in any manner. The amount of water is not the same in all areas. It is expressed by the average annual amount of precipitation in mm/year, which indicates how many mm of precipitation (“rain”} per 1 m
2
per year, in a particular area. 1 mm of precipitation is equivalent to 1 l of water.
The “production” of rainwater is 500 - 800 l per 1 m
2
per year.
Breakdown of household water consumption
-
32% ... personal hygiene - bathing, showering
-
8% ... minor hygiene - washing hands, etc.
-
2% ... cooking and drinking
-
8% ... washing up
-
50% ... potable water replaceable with rainwater
-
30% ... WC
-
12% ... laundering
-
4% ... garden irrigation
-
4% ... household cleaning
Average amount of precipitation in mm/year:
Prague 570; Brno 660; Olomouc 680; Ostrava 750; Plzeň 670
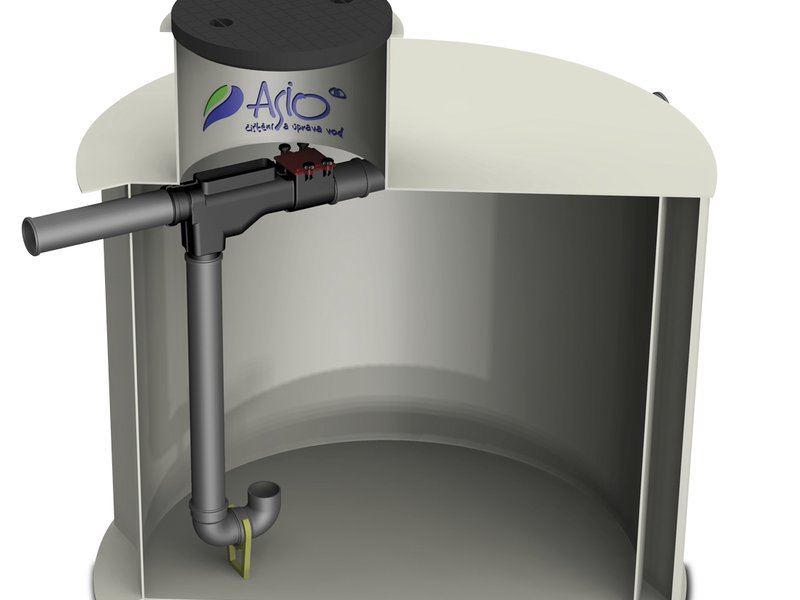
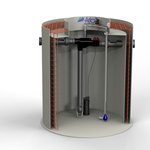
Gutter and gutter pipes
– drain captured rainwater from the roof.
Filter
– removes mechanical dirt from rainwater (e.g., leaves). It must have a corresponding efficiency and self-cleaning capability.
Tank pipeline
– directs treated water to the tank.
Tank
– above-ground or underground, accumulates rainwater; it should maintain a temperature below 16°C to limit the propagation of bacteria (underground tanks are convenient); it must have adequate strength and the inlet arranged in such a way that the dirt on the bottom should not be whirled up; it must have a safety overflow.
Replenishing unit
– adds potable water to the system in dry periods. It must ensure the separation of the distribution systems of potable water and rainwater.
Pump with a pressure switch or domestic pumping station
– maintains the pressure of rainwater in the system.
Rainwater distribution system
– transports rainwater to the places of consumption; it must be separated from the potable water distribution system.
Safety overflow
– drains water if the tank gets overfilled.
Pipeline to the sewerage system
– drains part of the water with the mechanical dirt.
Sewerage system
– drains excess rainwater or alternatively infiltration with the use of an
AS–NIDAPLAST
block.
Segments of a rainwater utilization system

AS–REWA Kombi (Compact Unit)
In a single unit it ensures:
-
Rainwater filtration
-
Rainwater accumulation
-
Pumping of rainwater to the distribution system
-
Replenishment of potable water to the system in the case of a precipitation shortage
It is delivered in standard sizes with an accumulation volume of 1.0 to 8.8 m
3
.
Tank design options:
-
Plastic, self-supporting,
-
Plastic for embedding in concrete,
-
Double jacketed for concreting
(plastic - insulation, concrete - supporting structure).

AS–REWA Kombi - technical data
- cylindrical


- rectangular


- double-jacketed


- double-jacketed, under level of ground water


AS–REWA ECO Compact Unit

AS–REWA ECO - technical data
- cylindrical


- rectangular


- double-jacketed
-
Underground double-jacketed tank
-
Self-supporting after installation (plastic-concrete combination)
-
Adapted for the installation of segments of the concrete inlet shaft


- double-jacketed, under level of ground water


Price
includes:
PP
tank
,
filter
AS
-
PURAIN
,
the input shaft
300 mm,
safety overflow
,
composite
cover
600 x
600
mm.
Price
does not include
: pump,
electrical
distribution
.