The technology for the treatment of the industrial wastewater produced in the furniture industry is able to separate aqueous paint as well as starch adhesives from the polluted industrial wastewater coming from the industrial process. The treatment technology can be used both for mixed wastewater (wastewater containing paint and adhesives) and for wastewater polluted by only residual paint or adhesives.
Advantages:
-
Minimal built-up area
-
Possibility of location near the production plant
-
Ability to separate both adhesives and paint in spite of a different technological procedure
-
Possibility to use existing tanks and pipelines
-
User-friendly system
-
No charges and fines for releasing polluted wastewater
-
Minimal operating costs
-
Return of investment in approx. 1-3 years
Use in various industrial branches:
-
Paper-making
-
Woodworking
-
Furniture
-
Construction
-
Textile
-
Printing
-
Automotive
Wastewater treatment principle in an AS-ASLI WWTP
The wastewater that is continuously released from the production plant is homogenized in an accumulation plant, where it is stirred with a slow-speed stirrer and pumped via a pipe mixer to a coagulation-sedimentation reactor. After homogenization, the wastewater always has approximately the same pollution quality.
In the pipe mixer, wastewater is adjusted with an alkaline stabilizer to the required pH value. Pollution is separated from wastewater through precipitation by the dosing of coagulant. In this way, the neutralization of wastewater to the required pH value is ensured, to comply with the requirements for water released into the sewerage system.
A more effective filtration capability and the dewatering of precipitated products in the filter press is achieved by the addition of organic flocculant. The treated wastewater complies with the requirements for the biological after-treatment of wastewater in a biological wastewater treatment plant.
Technological diagram:
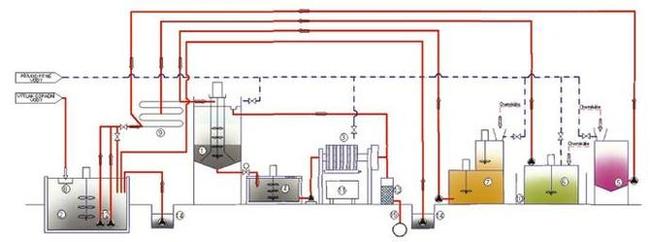
|
Legend:
1 Precipitation reactor
2 Accumulation tank
3 Dewatering of precipitated pollution
4 Homogenization sludge tank
5 Stabilizer – pH adjustment
6 Coagulant preparation
7 Flocculant preparations
|
8 Mechanical pre-treatment
9 Pipe mixer
10 Collection tub
11 Container
12 Sludge pumps
13 After-treatment filter
14 Underground dewatering sump
15 Drain into sewerage
|
FOR MORE DETAILED DATA ASK FOR DESIGN AND INSTALLATION DOCUMENTATION!
Selected references
|
Investor
|
Location
|
Capacity Q (m
3
/den)
|
Date of implementation
|
|
AGROP
|
Ptení, CZ
|
5
|
2001
|
|
KRONODOOR
|
Jihlava, CZ
|
10
|
2002
|
|
KRONOSPAN
|
Jihlava, CZ
|
10
|
2004
|
|
JITONA, a.s. IKEA
|
Klatovy, CZ
|
5
|
2004
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|






